T-Shirt bags
Plastic shopping bags, particularly the commonly used “T-shirt” bags, have become a central part of retail environments worldwide. Their lightweight design and affordability make them a convenient option for both consumers and businesses. However, as their ubiquity has grown, so too have concerns regarding their environmental impact. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the manufacturing journey of these plastic shopping bags, examining the materials, production processes, and environmental considerations involved.
- Primary plastic raw materials.
- No toxic additives.
- The packaging film is elastic, flexible and tear-resistant and does not stick to your hands.
R28-450 L

mm
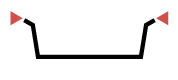
145,6 x 120,6

130.0 x 105,0

111,5 x 86,5

40,0

450 cc
R25-560 L

mm
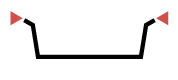
157,5 x 157,5

140,0 x 140,0

118,0 x 118,0

33,0

535 cc
R65-650 L

mm
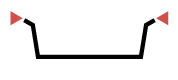
221,5 x 129,5

205,0 x 113,0

188,0 x 96,0

34,0

670 cc
R87-651 L

mm
218,6 x 126,6

203,0 x 111,0

187,0 x 95,0

33,0

620 cc
Raw Materials: The Foundation of Plastic Bags
The primary raw material used in the production of plastic shopping bags is polyethylene. Polyethylene can be produced in various forms, but the most common types used for shopping bags are:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): This material is favored for its durability and strength, despite being thin and lightweight. HDPE is commonly used to produce the standard T-shirt style bags found in grocery stores.
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE): LDPE produces thicker, more flexible bags. These are often used for items requiring heavier-duty carrying, such as boutique shopping bags.
Polyethylene is made through a polymerization process, where ethylene gas is transformed into plastic resin pellets. These pellets serve as the foundation for the plastic bag production process.
The Manufacturing Process
The production of plastic shopping bags involves several key steps:
- Extrusion: The process begins with the extrusion of polyethylene resin pellets. These pellets are heated until they melt into a thick, viscous liquid. This liquid is then forced through a narrow die, forming a thin, tubular film of plastic. This film will eventually become the body of the plastic bag.
- Blowing: After extrusion, the tube of plastic is inflated, a process called blown film extrusion. Air is blown into the tube to stretch the plastic into a large bubble, which cools and solidifies the film. By controlling the air pressure and the thickness of the film, manufacturers can produce bags of different strengths and sizes.
- Cutting and Sealing: Once the film has cooled, it is flattened and fed through a machine that cuts and seals the film into bag shapes. The characteristic T-shirt shape with two handles is cut out during this phase. These handles are an essential feature of the bag’s design, allowing easy carrying and versatility. During the cutting and sealing process, machines use heat to fuse the edges of the plastic film, forming the seams that give the bags their strength. This step ensures that the bags can handle the weight of groceries or other items without tearing easily.
